iPSC-derived MASLD model
Our in vitro MASLD model represents an optimized cell platform for drug discovery applications and a principal tool for elucidating the underlying mechanisms of the disease
Metabolic dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
MASLD is a spectrum of disease ranging from lipid accumulation within hepatocytes to steatohepatitis with inflammation (MASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and can eventually lead to the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Using our proprietary Ulti-HEP platform, we have developed a novel in vitro MASLD model that recapitulates the disease phenotype in-a-dish, offering an optimized model for drug discovery applications and a principal tool for elucidating the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
.jpg?width=2000&name=image%20(3).jpg)
Limitations in animal and primary cell models
Current animal and primary hepatocyte models used to study MASH and MASLD, are widely used because they replicate certain aspects of human metabolic processes. These models often use high-fat diets or genetic modifications to induce MASLD.
Do not recapitulate human metabolism
Other models do not fully mimic the complexity of human metabolism or the multifactorial nature of the condition. This gap limits the translation of findings to human clinical outcomes leading to unsuitable compounds being selected for during screening investigations.
Unsuitable for high throughput screening
Primary hepatocyte models, offer more human-relevant insights, particularly when used in co-cultures. While they are useful for studying inflammation, fibrosis, and lipid metabolism, these cells have limitations such as short lifespan, loss of functionality in culture, and donor variability, which can affect reproducibility and scalability.
Our Ulti-HEP cells accurately recapitulates the MASLD phenotype when they are treated with high-sugar or high-fat diets, whilst also being scalable and sourced from a single donor, thereby generating reproducible data.
Our Ulti-HEP model de-risks drug discovery by providing a new and highly predictive in vitro screening platform suitable for high throughput studies.

Ulti-HEP are phenotypically relevant
When our Ulti-HEP cells are treated with high glucose or high fat diets, they demonstrate increased lipid accumulation, insulin resistance, lipotoxicity and inflammation. This makes them an accurate and ideal human derived model to screen compounds in high throughput investigations.
Lipid accumulation
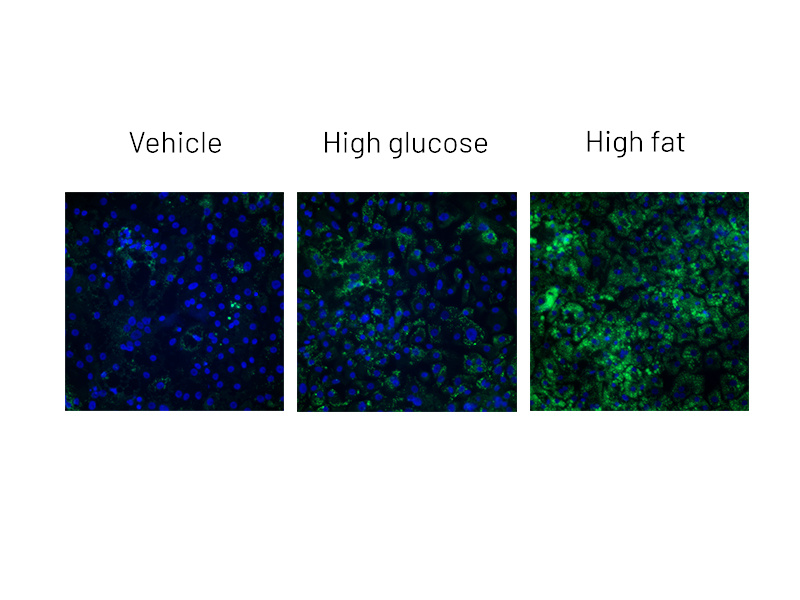
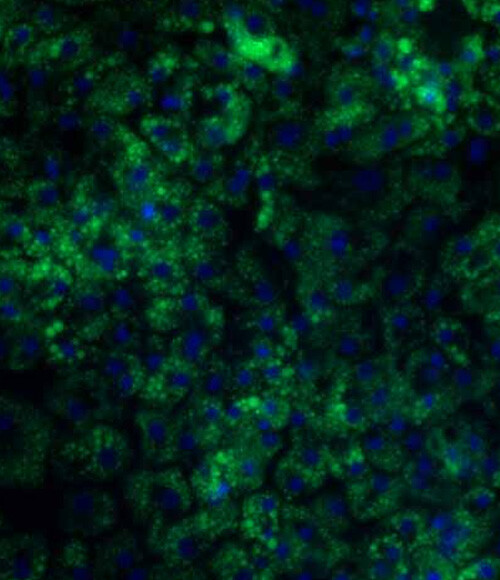
Figure 2a: BODIPY staining on DefiniGEN Ulti-HEP demonstrating increased lipid accumulation following 5 days of treatment with glucose and free fatty acids
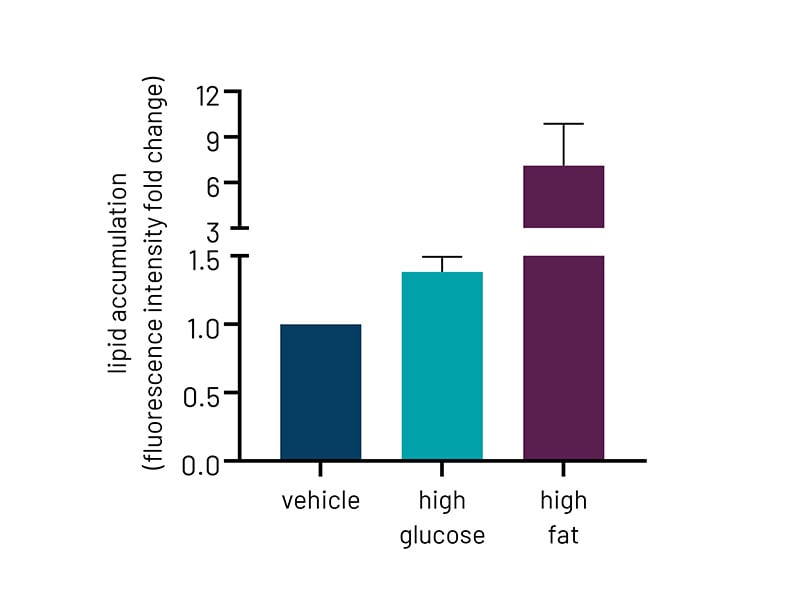
Figure 2b: Quantification of lipid accumulation of Ulti-HEP following 5 days of treatment with glucose and free fatty acids as measured by BODIPY staining in Fig 2a. Fluorescence intensity was normalized to total nuclei number. All data are presented as mean ±SEM of n=3 independent experiments.
Insulin sensitivity
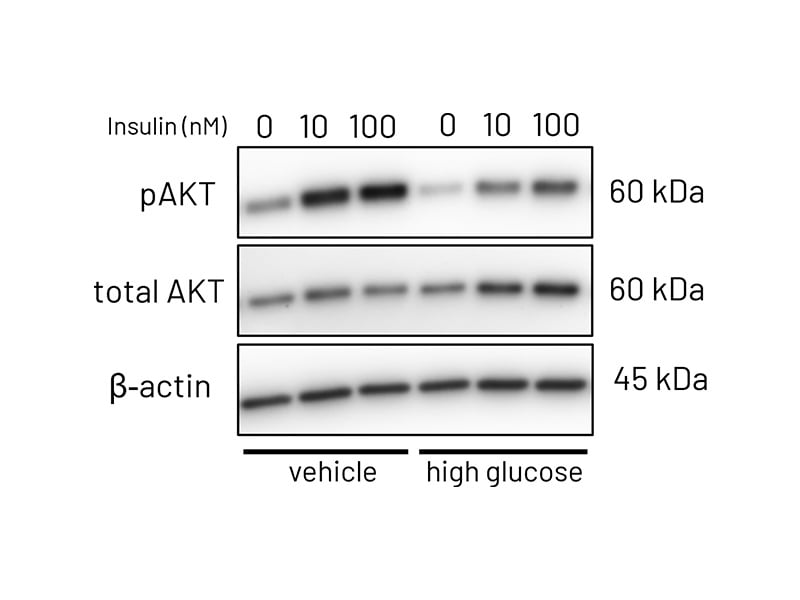
Figure 3a: Representative western blot images demonstrating phosphorylation of AKT following stimulation with increasing concentrations of insulin (10-100nM) in vehicle treated and high-glucose treated Ulti-HEP.
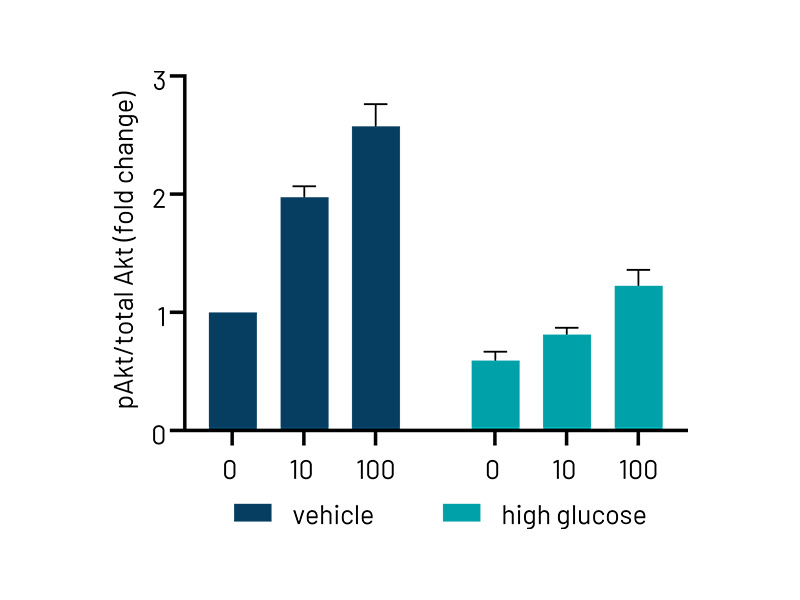
Figure 3b: Quantification of western blotting in vehicle and high-glucose treated Ulti-HEP. The data demonstrates reduced phosphorylation of AKT in high-glucose treated cells, indicative of hepatic insulin resistance. Protein data were normalized to total AKT and beta-actin and are presented as mean ±SEM of n=3 independent experiments.
Lipotoxicity and inflammation
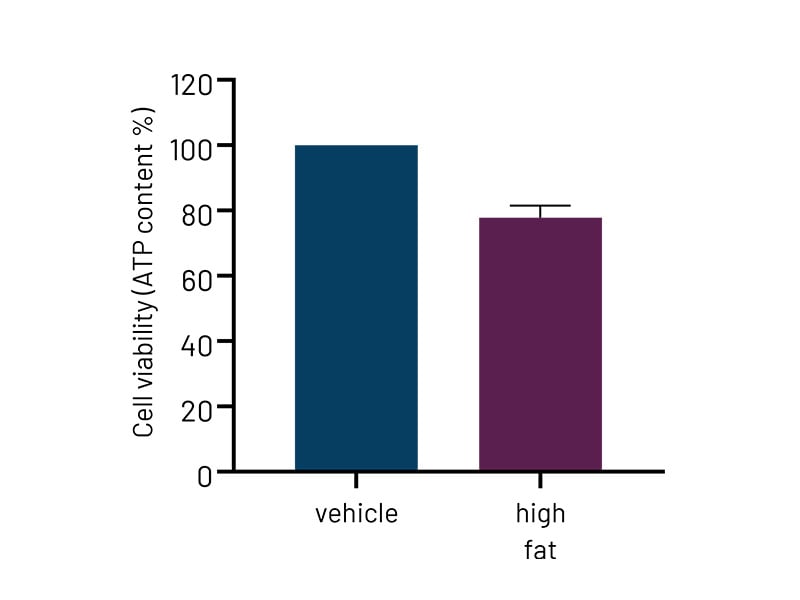
Figure 4a: High-fat-treated DefiniGEN Ulti-HEP demonstrate reduced cell viability compared to vehicle-treated cells, indicative of enhanced lipotoxicity. .
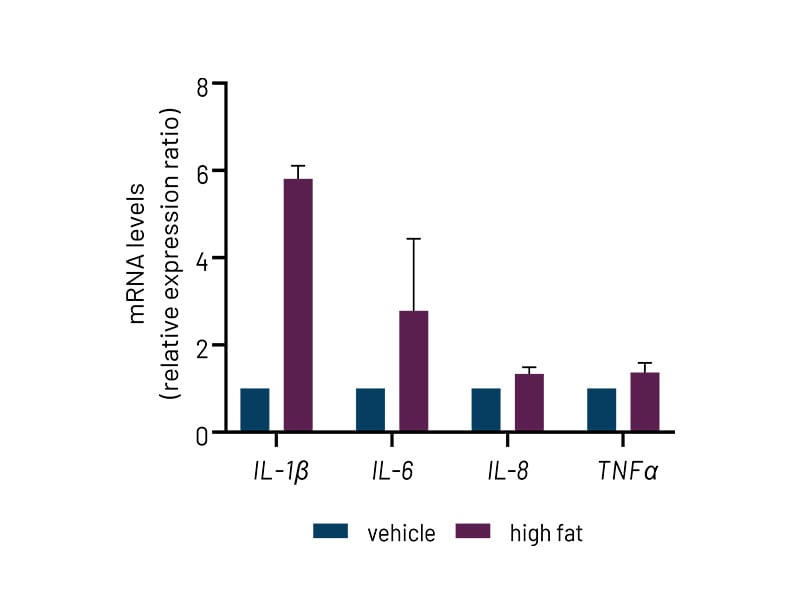
Figure 4b: High-fat-treated DefiniGEN Ulti-HEP demonstrate increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine markers (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNFα) compared to vehicle-treated cells. mRNA data were normalized to 18S rRNA. All data are presented as mean±SEM of n=2-3 independent experiments.
MASLD-associated gene variants
In the last 20 years, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified common single-nucleotide polymorphisms in a variety of genes as main determinants of MASLD.
Of those, the most common disease-implicated genetic variant is I148M in the gene coding for Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3). Using CRISPR/Cas9 technology, we have generated gene-edited Ulti-HEP models carrying the I148M mutation and demonstrated the detrimental effects of genetic variation on MASLD development.
This cell line is ideally suited for researchers who are specifically interested in modelling or screening compounds against hepatocytes with the PNPLA3 mutation. As with our wildtype Ulti-HEP cells, this mutated cell line is human-derived and source from a single donor, allowing you to scale your research as necessary whilst maintaining no batch-to-batch variation between cells.
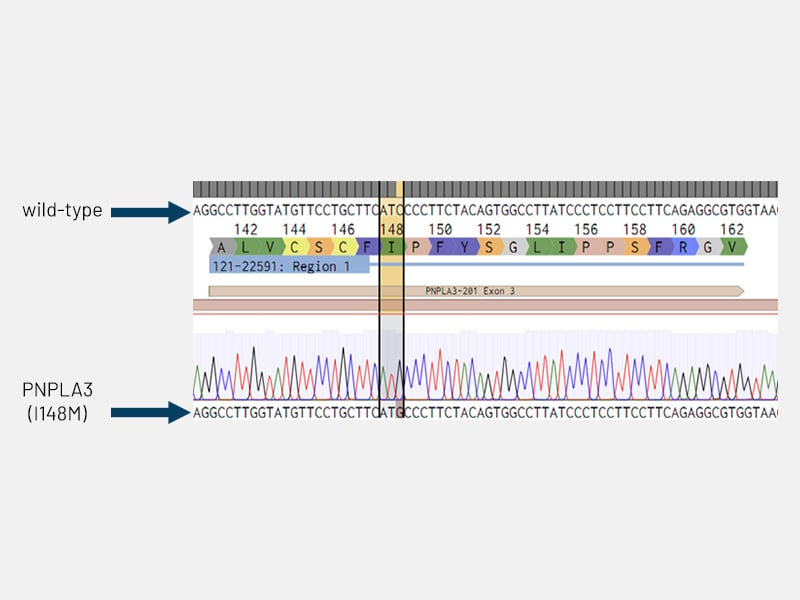
Figure 5: Disease circuit - Sanger sequencing chromatogram confirming the insertion of the PNPLA3 I148M mutation (ATC>ATG; isoleucine to methionine) in DefiniGEN Ulti-HEP.
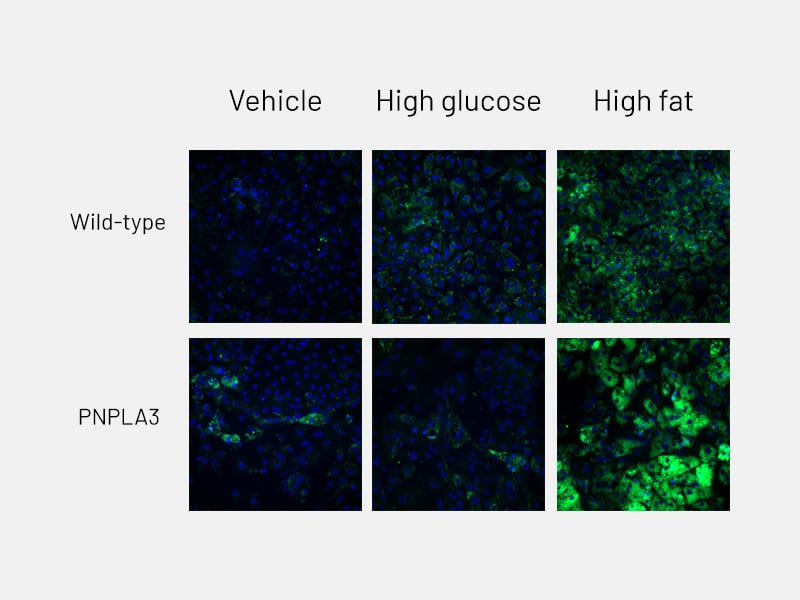
Figure 6a: Lipid accumulation - Lipid accumulation in wild-type and PNPLA3-mutant Ulti-HEP following 5 days of treatment with glucose and free fatty acids, as measured by BODIPY staining.
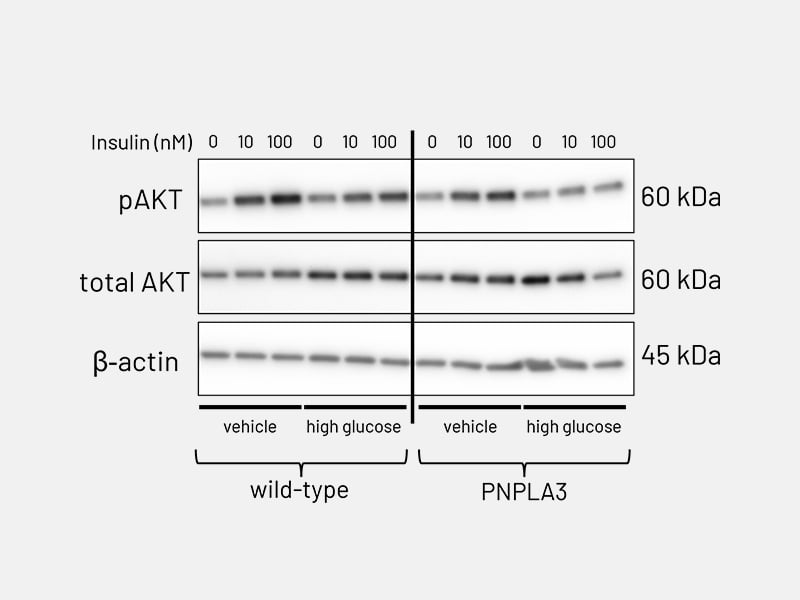
Figure 6b: Lipid accumulation - AKT phosphorylation in PNPLA3-mutant Ulti-HEP following stimulation with increasing concentrations of insulin (10-100nM), revealing impaired response to insulin compared to wild-type Ulti-HEP.


