iPSC-Derived PFIC2 Cells for Screening
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a heterogeneous group of autosomal recessive liver diseases, characterized by mutations in genes involved in hepatocellular bile acid secretion
The global prevalence of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis (PFIC) is estimated to be between 1 in 50,000 and 1 in 100,000 live births1. Amongst these, PFIC2, caused by mutations in the ABCB11 gene, represents half of the total PFIC cases and suffer from liver failure, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Due to the lack of appropriate pre-clinical models in drug discovery, DefiniGEN have developed the world’s first novel iPSC-derived hepatocyte system for large-scale screening that recapitulates the human PFIC2 phenotype in-a-dish, offering, for the first time, an effective pre-clinical PFIC2 disease model for hit-lead drug screening studies.
Advantages to using our PFIC2 iPSC-derived cells
Until now, most studies have been performed on ABCB11 knockout mice models. However, there is evidence that these models demonstrate a compensatory increase in the expression of other transporters (e.g., ABCB1/MDR1), which is not observed in humans2. This severely reduces the likelihood that any compounds successfully screened using these models will demonstrate similar efficacy in humans. Similarly, primary human hepatocytes have failed to show promise due to the limited access to patient-derived cells and the inherent genetic variation between different donors, even if these could be sourced in sufficient quantities. Finally, commonly used hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines, such as HepG2, do not express the ABCB11 transporter, which means they cannot be used for disease modelling development.
Through CRISPR-Cas9 technology, we have introduced the D482G mutation into the ABCB11 gene, to create a human iPSC-derived PFIC2 disease model. These cells possess many advantages over the currently available models widely used to study the disease, as summarized below:
|
Cell type |
Source |
Biologically relevant to humans? |
Available in quantities necessary for screening? |
No batch-to-batch variation? |
Gives reproducible data? |
|
iPSC-derived PFIC2 cells |
Single human donor |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Mouse derived models |
Mouse models |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Primary human hepatocytes |
Multiple human donors |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines |
Multiple human donors |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Screening with iPSC-derived PFIC2 cells with DefiniGEN
Consultation
Speak to one of our experts to discuss your research needs and to arrange delivery of your compounds or gene delivery systems. We can accept:
- siRNA
- mRNA
- DNA plasmids
- Lentiviral vectors
- Adeno-associated Vectors (AAVs)
- GalNAc conjugates
- Other systems can be accepted on request

Screening
Our experts will screen your compounds or gene delivery systems according to the agreed experimental design. After understanding your needs, we will closely work with you to define the best experimental conditions that are required to answer your scientific questions. To achieve this, we have extensively validated our cell models against a wide range of state-of-the art readout assays with the aim to deliver successful outcomes efficiently and in a cost-effective manner.
Reporting
Throughout the duration of the project, our scientists will provide you with updates related to the progress of your experiments. At the end of the project, a detailed report is shared with you discussing the applied methodology and presenting the results of the screening. For custom cell model generation, additional Certificates of Analysis (CoA) will be shared with you, providing a detailed characterization of the cell lines.

If you are looking for standardized, phenotypically relevant PFIC2 human models to screen compounds or gene delivery systems against, contact one of our experts today.
Technical data
Our cells are highly characterized and are sourced from a single donor to give accurate and reproducible data with no batch-to-batch variation.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived PFIC2 iPSCs carry the D482G mutation without any effect in pluripotency status
A

B
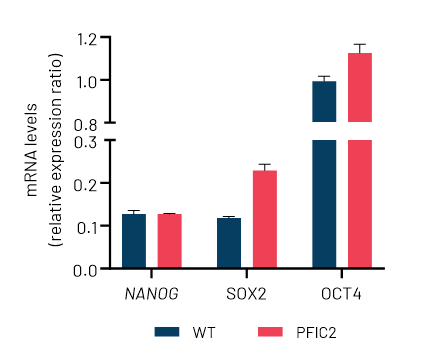
Figure 1: A) Sanger sequencing showing wild-type (top sequence) and mutated iPSCs (bottom sequence) carrying the D482G mutation (GAT>GGT) in the ABCB11 gene. The codon change is highlighted with yellow. B) mRNA expression levels of the key pluripotency markers NANOG, SOX2, and OCT4 in wild-type (WT) and CRISPR-derived ABCB11 iPSCs (PFIC2). mRNA data were normalized to GAPDH and are presented as mean±SEM of n=3 biological replicates.
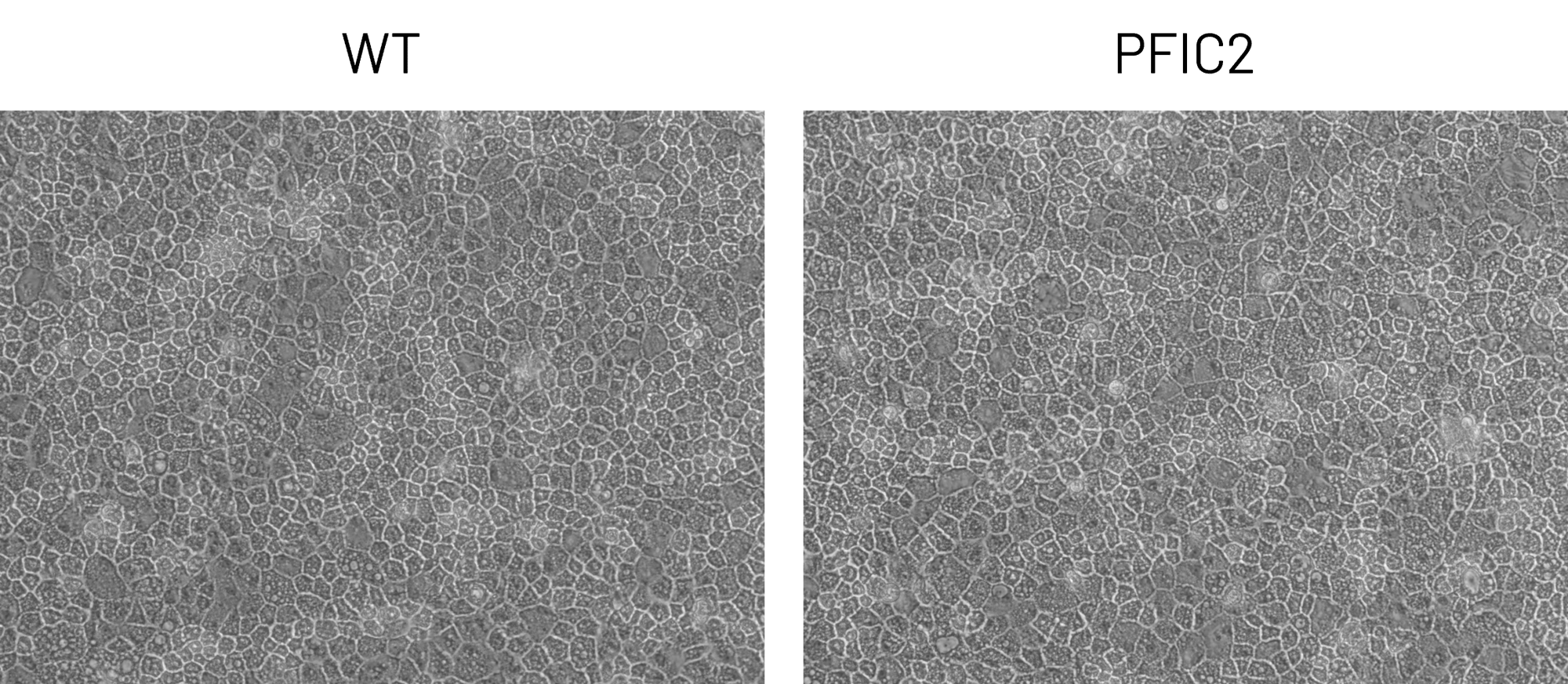
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived PFIC2 iPSCs successfully differentiate to Ulti-HEP
A
B
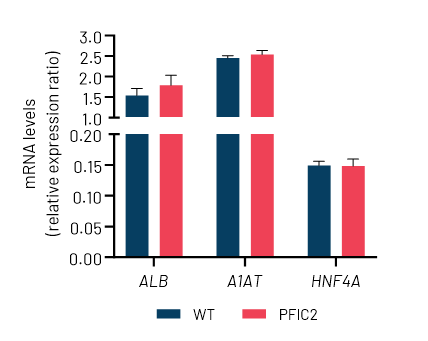
Figure 2: A) Representative images demonstrating the characteristic hepatocyte cobblestone morphology in wild-type (WT) and PFIC2 Ulti-HEP. B) mRNA expression levels of the hepatocyte maturity markers albumin (ALB), alpha-1-antitrypsin (A1AT), and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4A (HNF4A) in wild-type (WT) and PFIC2 Ulti-HEP. mRNA data were normalized to PPIA and are presented as mean±SEM of n=2 biological replicates.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived PFIC2 Ulti-HEP demonstrate reduced ABCB11 mRNA and protein expression
A
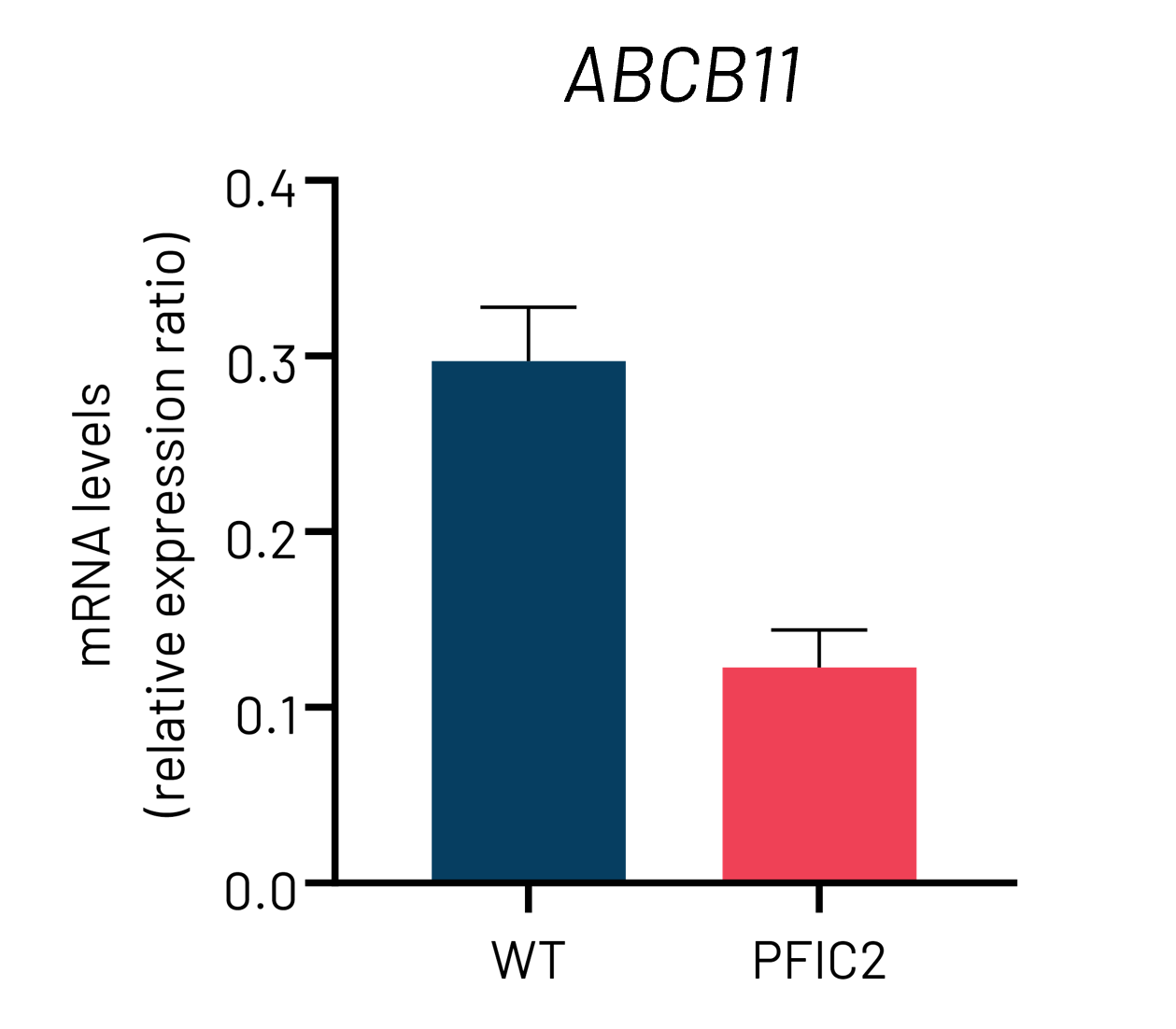
B
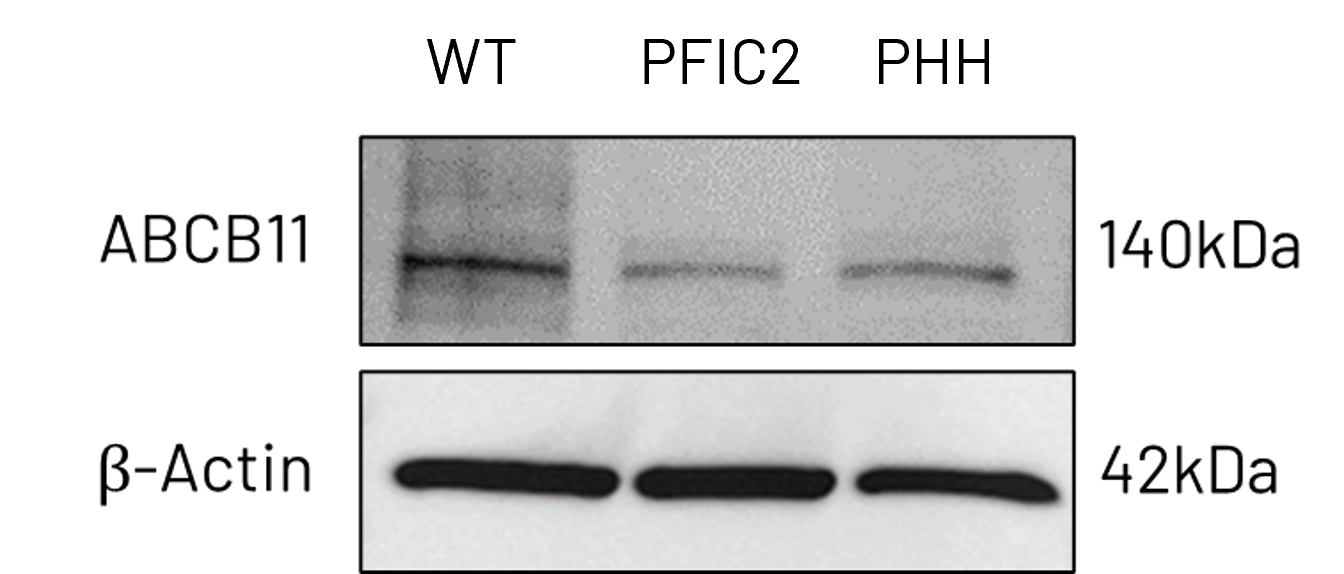

Figure 3: A) mRNA expression levels of ABCB11 in wild-type (WT) and PFIC2 Ulti-HEP cultured in transwell culture system. B) Protein expression levels of ABCB11 in transwell-cultured WT and PFIC2 Ulti-HEP in comparison to primary human hepatocytes (PHH). mRNA data were normalized to 18S rRNA, and protein data to β-actin. All data are presented as mean±SEM of n=3-4 biological replicates.
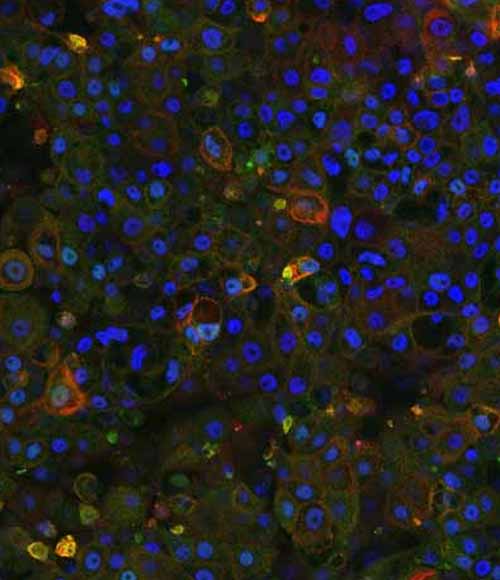
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived PFIC2 Ulti-HEP exhibit disrupted ABCB11 localization
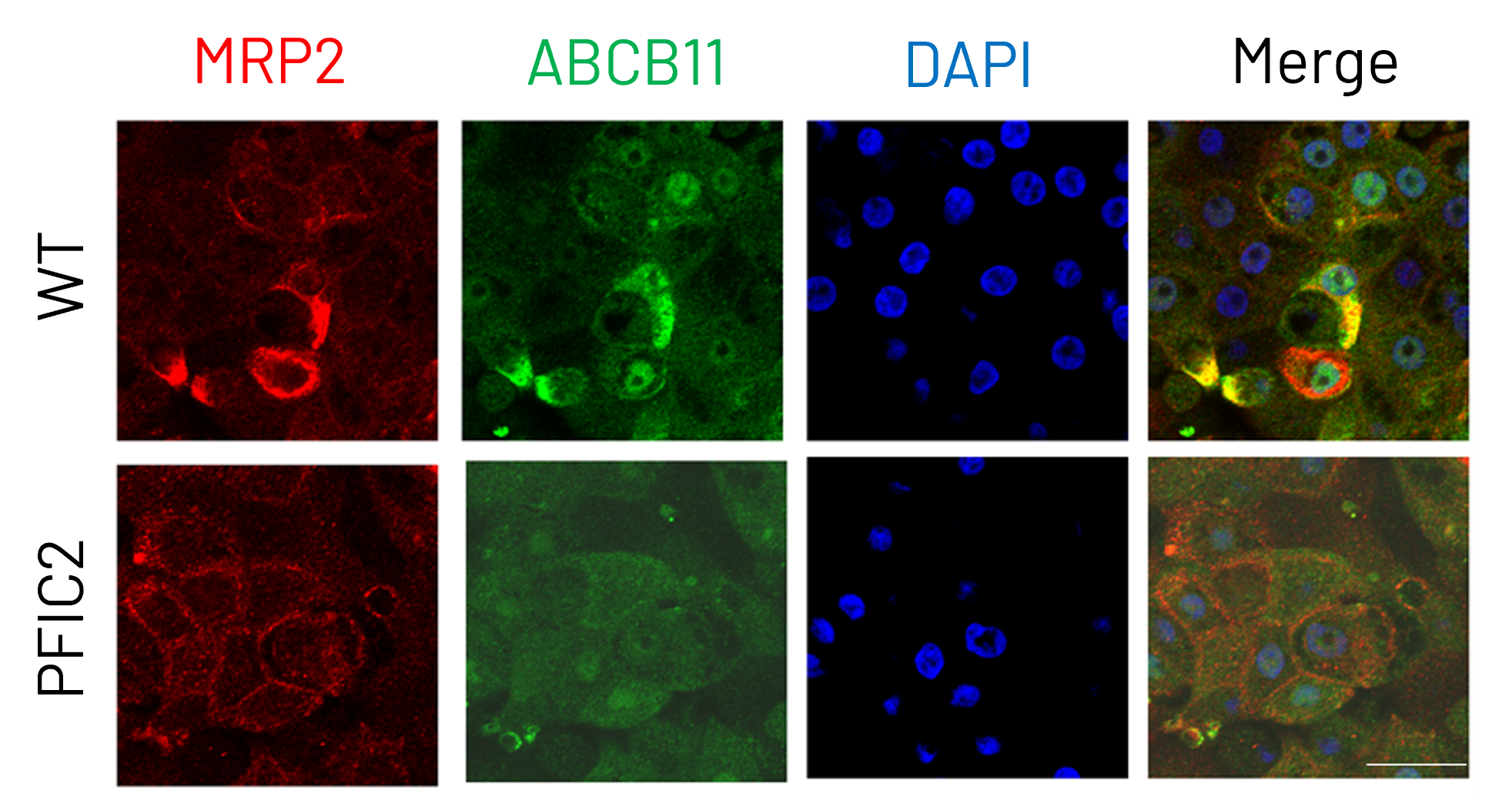
Figure 4: Immunocytochemistry analysis of MRP2 (red) and ABCB11 (green) in wild-type (WT) and PFIC2 Ulti-HEP cultured in transwell culture system. Scale bar: 50 µm.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived PFIC2 Ulti-HEP demonstrate reduced bile acid transport
A
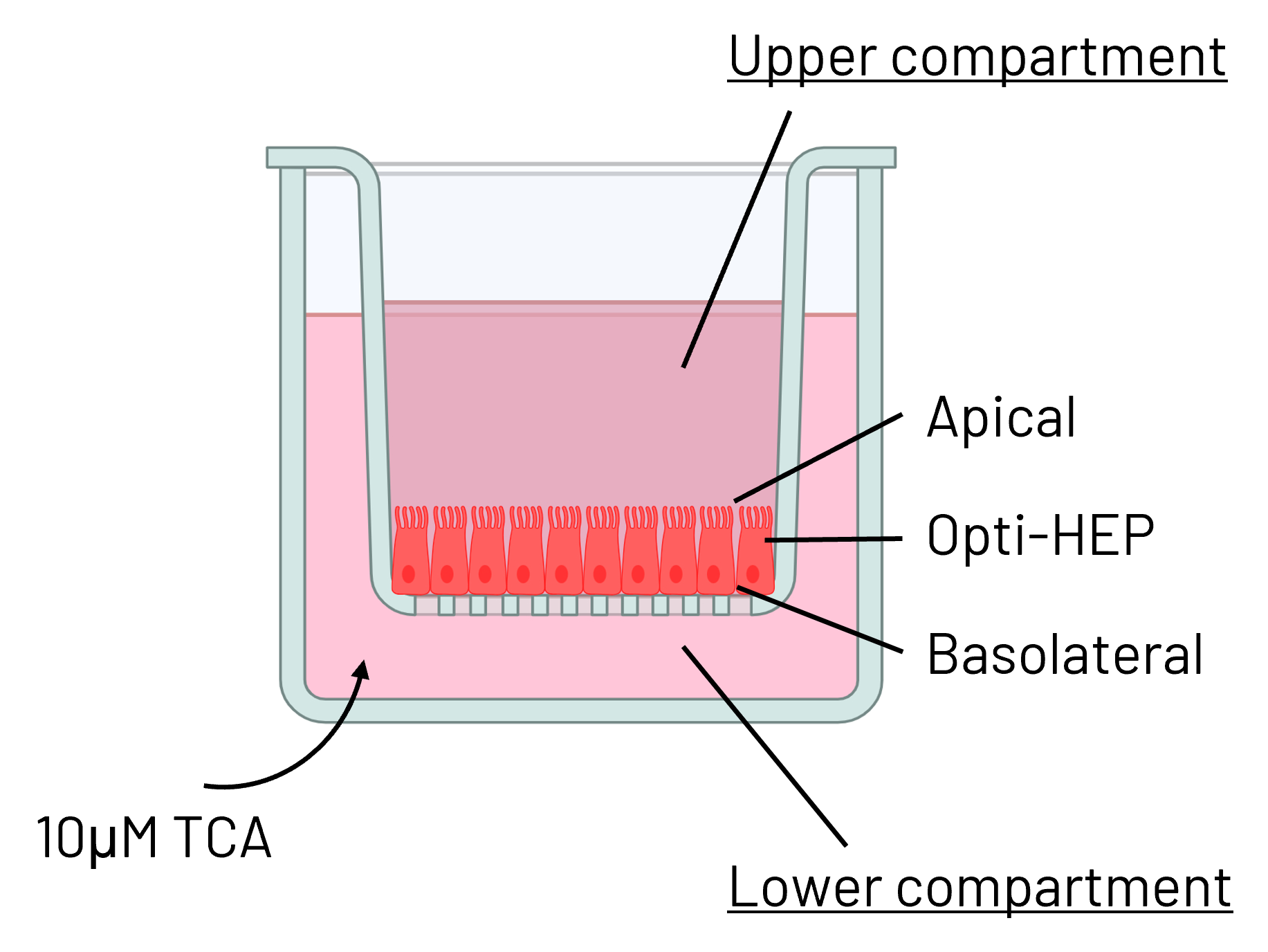
B
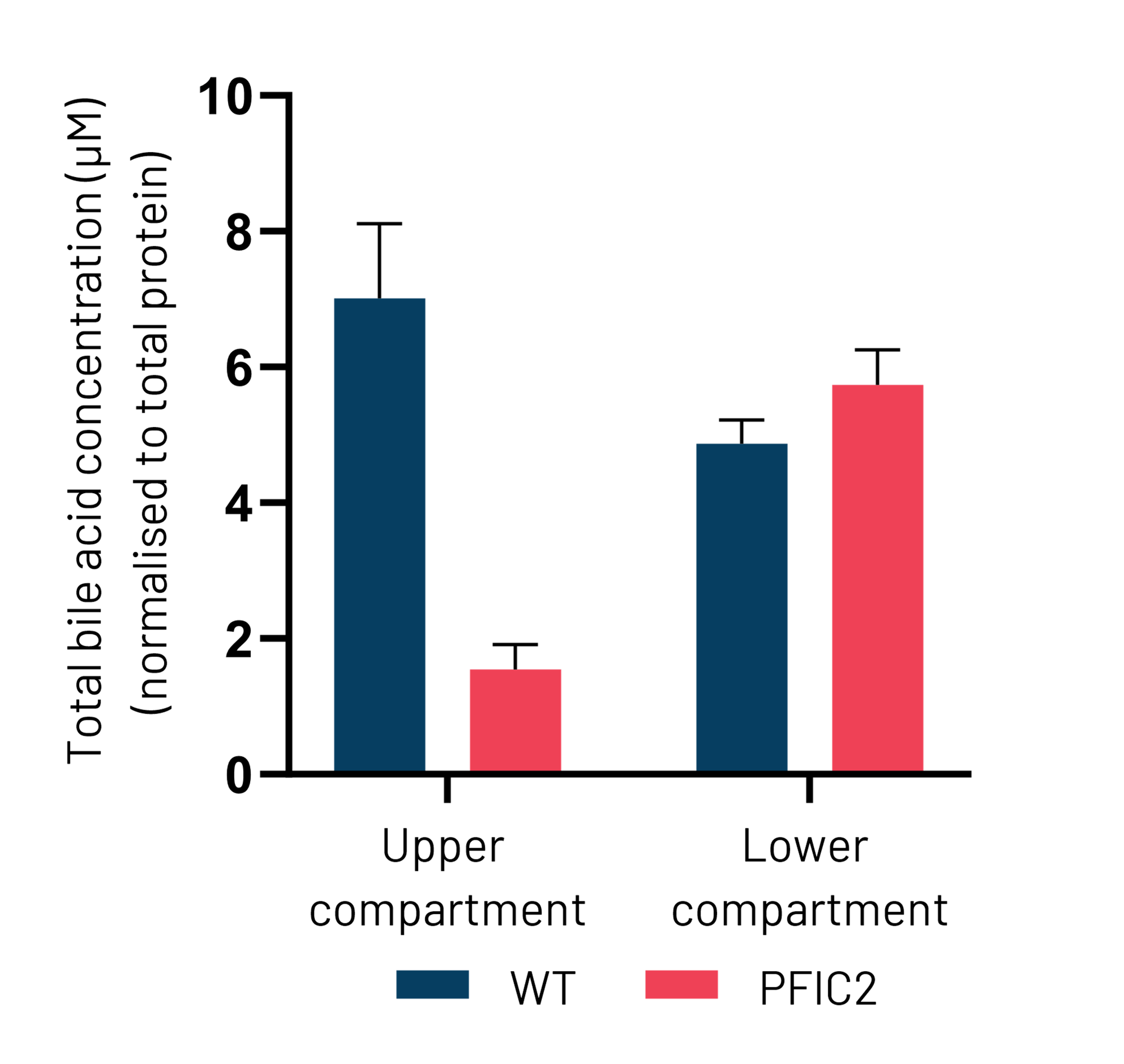
Figure 5: (A) Schematic depiction of Ulti-HEP polarization cultured in transwell culture system. (B) Taurocholic acid (TCA) quantification in the upper and lower transwell compartments of WT and PFIC2 Ulti-HEP following 48 hours of TCA addition (10 μM) to the lower compartment, indicating dysfunctional ABCB11 activity in the PFIC2 cells. Data are presented as mean±SEM of n=4 biological replicates.
If you are looking for standardized, phenotypically relevant PFIC2 human models to screen compounds or gene delivery systems against, contact one of our experts today.

