Liver
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency
Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency is an inherited, X-linked, recessive metabolic disorder and, currently, the most common UCD with a prevalence of one in 60-70,000 in humans.
It is mainly caused by mutations on the OTC gene, which encodes the mitochondrial enzyme ornithine transcarbamylase. There are no prevalent mutations in the human population, and most of them are distributed throughout the gene. Due to difficulties in developing iPSC- derived hepatocytes with a functional urea cycle pathway, no in vitro disease models for OTC deficiency are available to date.
Functional urea cycle pathway
Our iPSC-derived hepatocyte wild type, Ulti-HEP, demonstrate functional urea cycle pathway
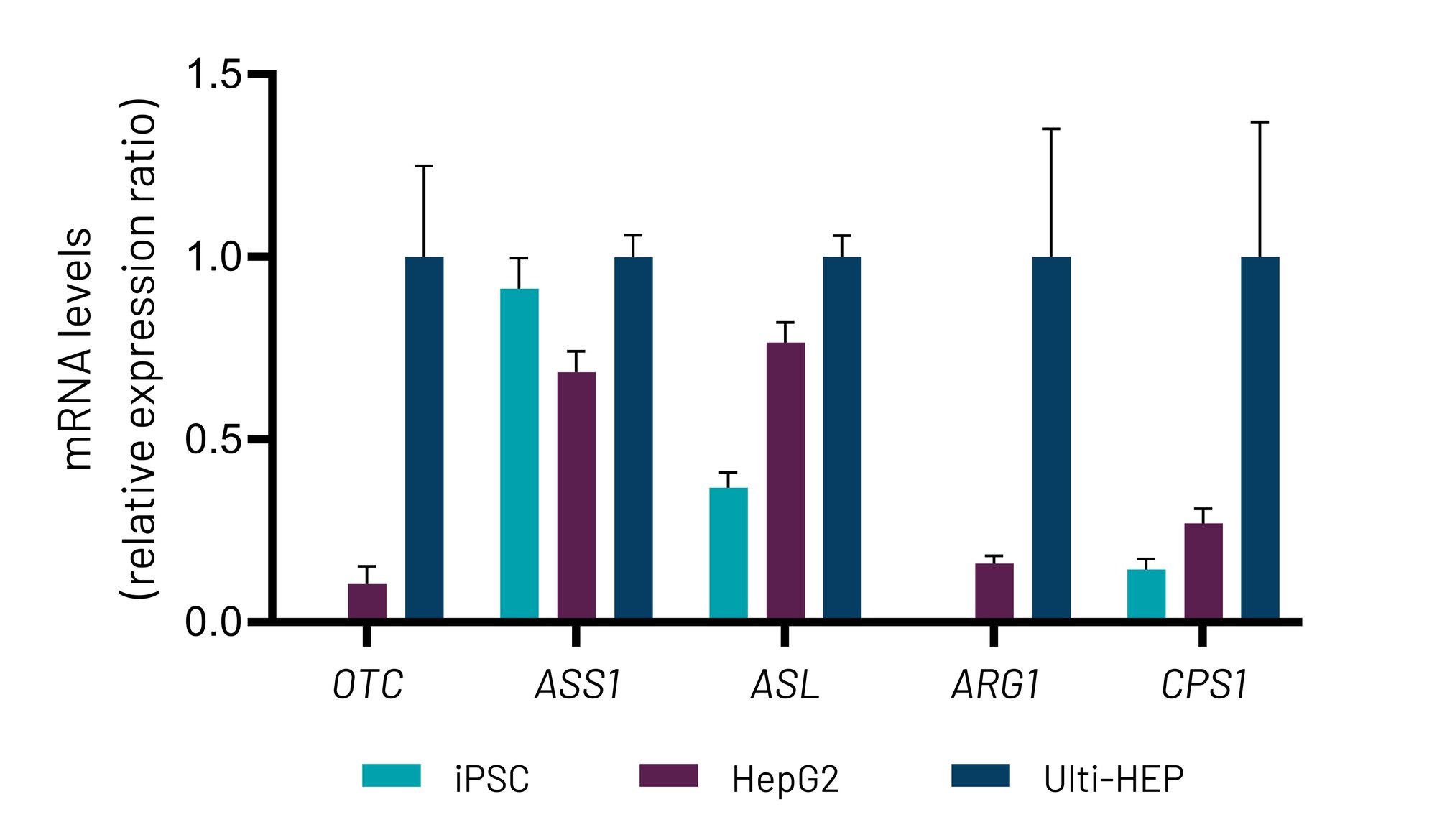

Figure 1. A) mRNA expression levels of the five urea cycle genes in wild-type induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), liver carcinoma HepG2 cells, and DefiniGEN Ulti-HEP. B) Protein expression levels of the five urea cycle enzymes in liver carcinoma HepG2 cells and DefiniGEN Ulti-HEP. mRNA data were normalized to 18S rRNA and are presented as mean±SEM of n=3 biological replicates.
DefiniGEN iPSC-derived wild-type hepatocyte-like cells secrete urea in a time-dependent manner
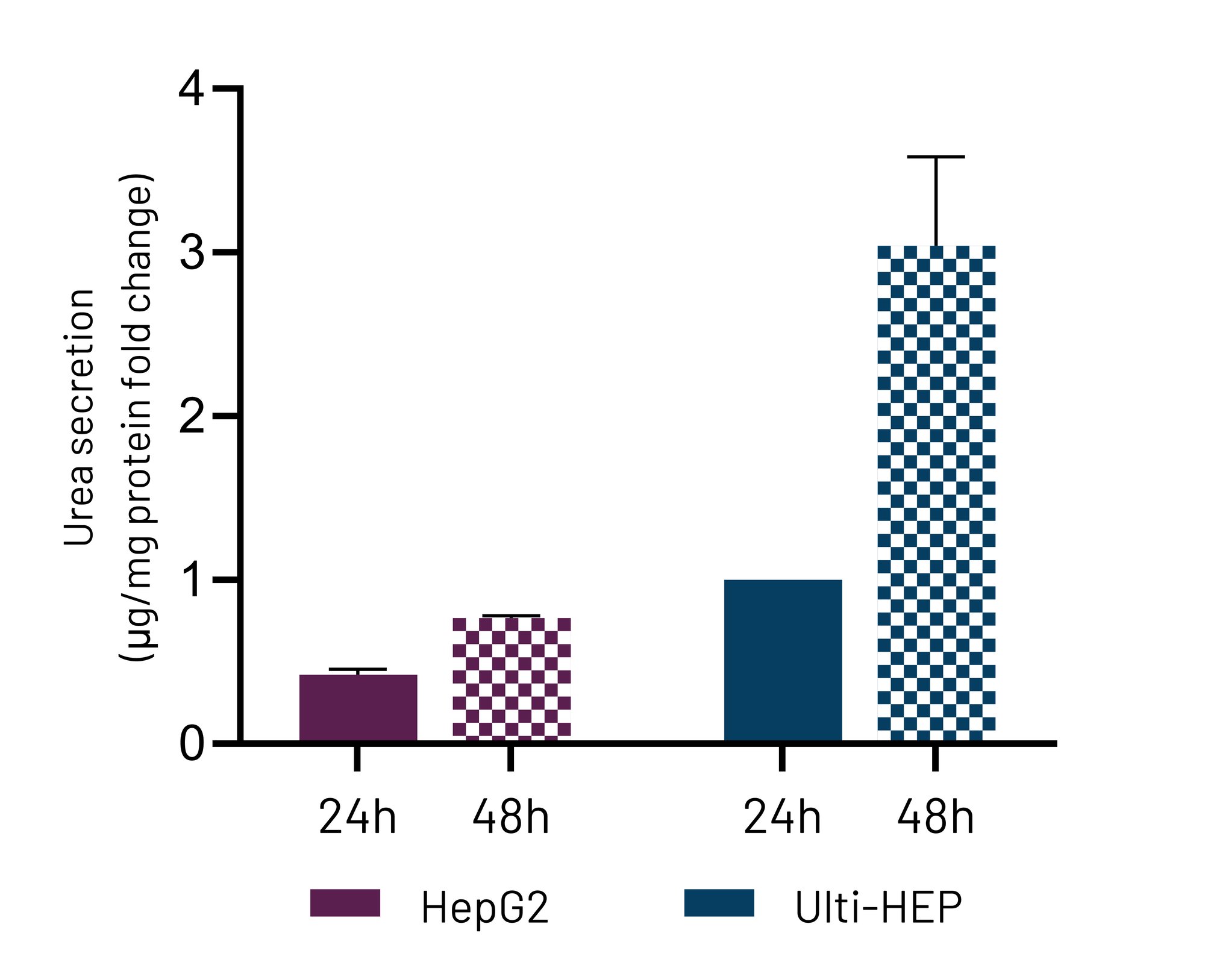
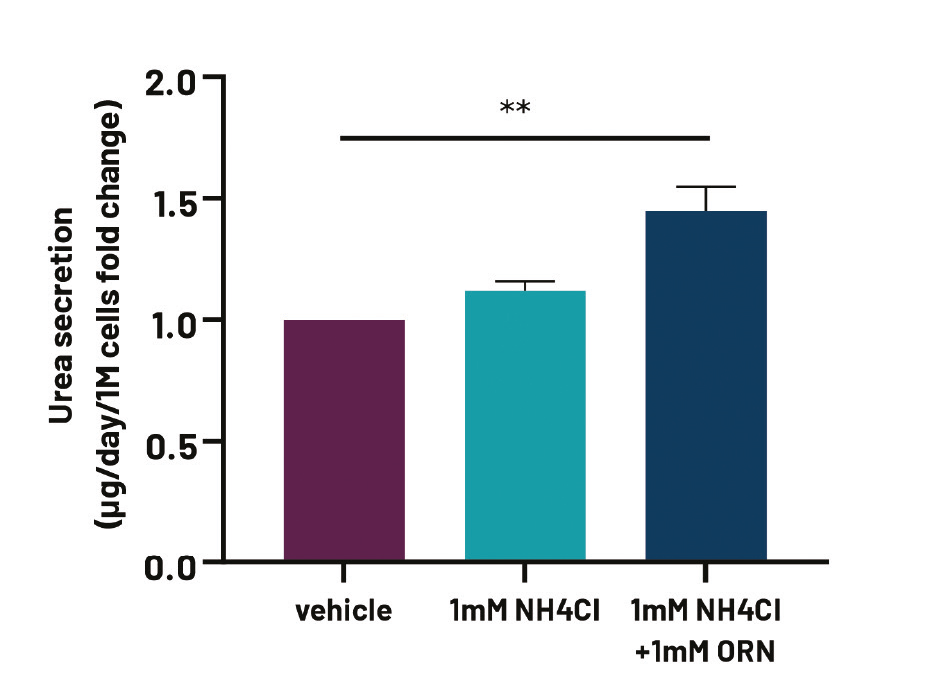
Figure 2. Media urea levels in high oxygen-cultured Ulti-HEP and HepG2 cells for 24h and 48h. Data were normalised to total protein levels and are presented as mean±SEM fold change of n=3 biological replicates. **p<0.01.
Figure 3. Media urea levels in high oxygen-cultured Ulti-HEP in the presence of either vehicle, 1mM NH4Cl, or 1mM NH4Cl +1mM Ornithine for 24h, suggestive of functional OTC activity. Data were normalised to total cell number and are presented as mean±SEM fold change of n=3 biological replicates. **p<0.01.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived OTC deficiency (OTCD) Ulti-HEP carry the D175V mutation
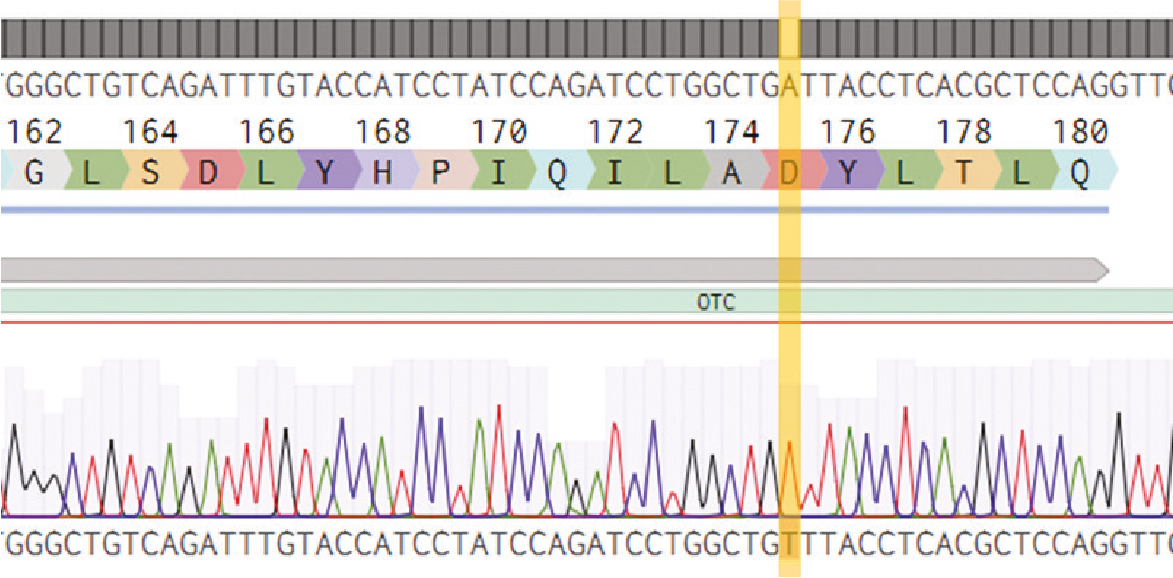
Figure 4. Sanger sequencing showing healthy wild-type (top sequence) as well as mutated iPSCs (bottom sequence) carrying the D175V mutation (GAT>GTT) on the OTC gene. The codon change is highlighted with yellow.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived OTCD iPSCs successfully differentiate to Ulti-HEP
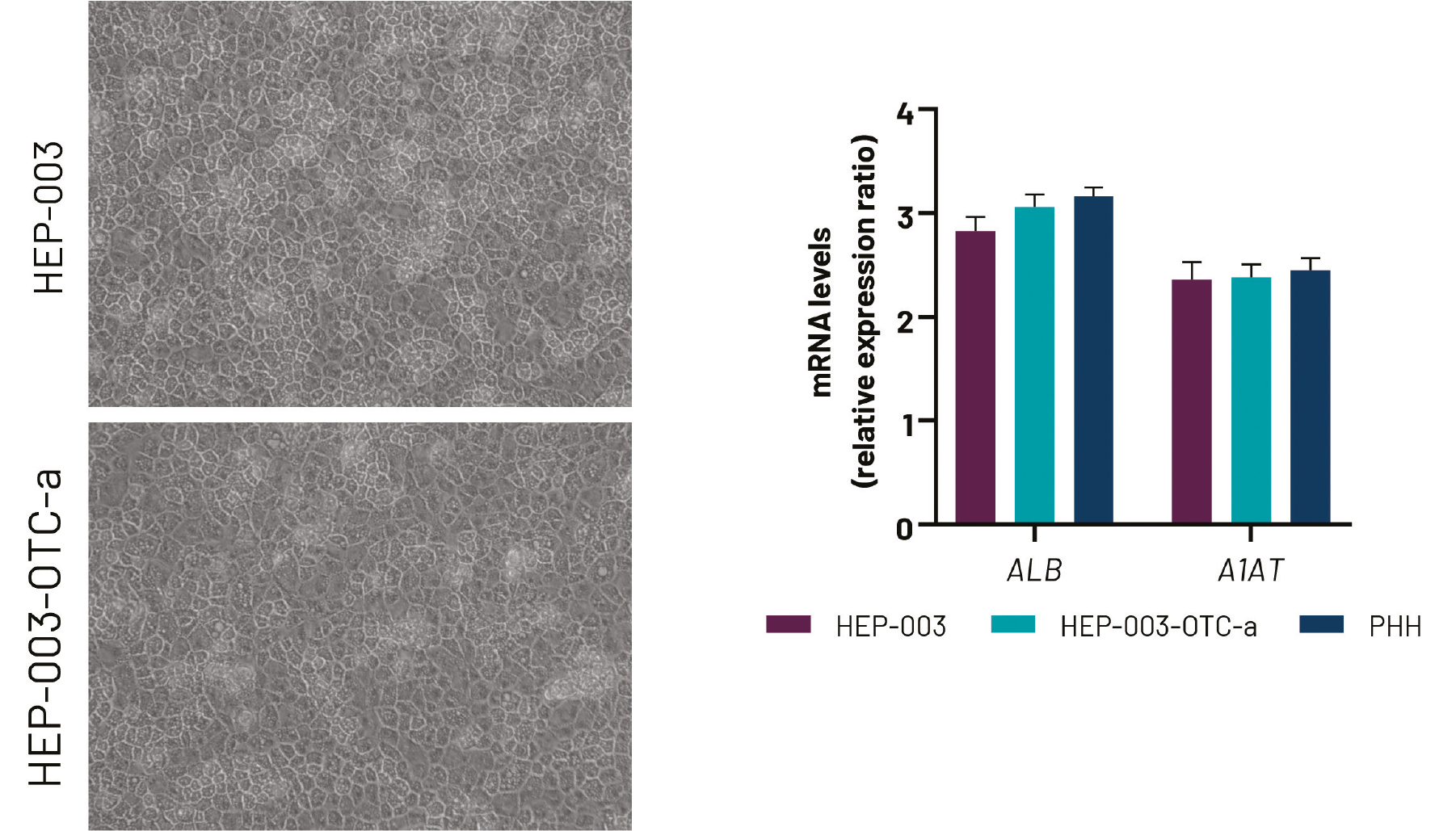
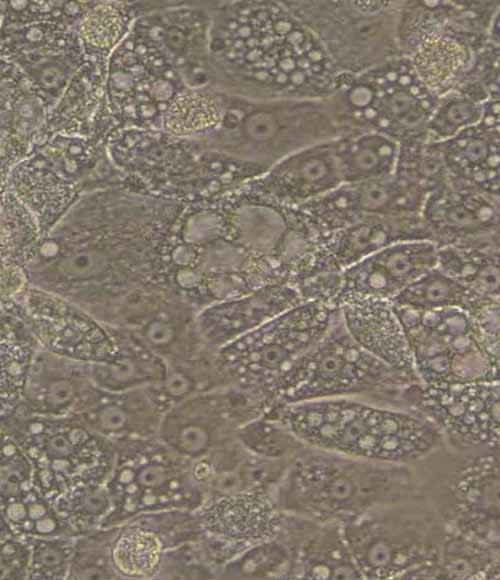
Figure 5. A) Representative images demonstrating the characteristic hepatocyte cobblestone morphology in wild-type (HEP-003) and OTCD (HEP-003-OTC-a) iPSC-derived hepatocytes (Ulti-HEP). B) mRNA expression levels of the hepatocyte maturity markers albumin (ALB) and alpha-
1-antitrypsin (A1AT) in wild-type Ulti-HEP (HEP-003), OTCD Ulti-HEP (HEP-003-OTC-a), and primary human hepatocytes (PHH). mRNA data were normalised to PPIA and are presented as mean±SEM of n=3 independent experiments. Objective: 10x.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived OTCD Ulti-HEP demonstrate decreased OTC protein expression and urea secretion compared to wild-type Ulti-HEP
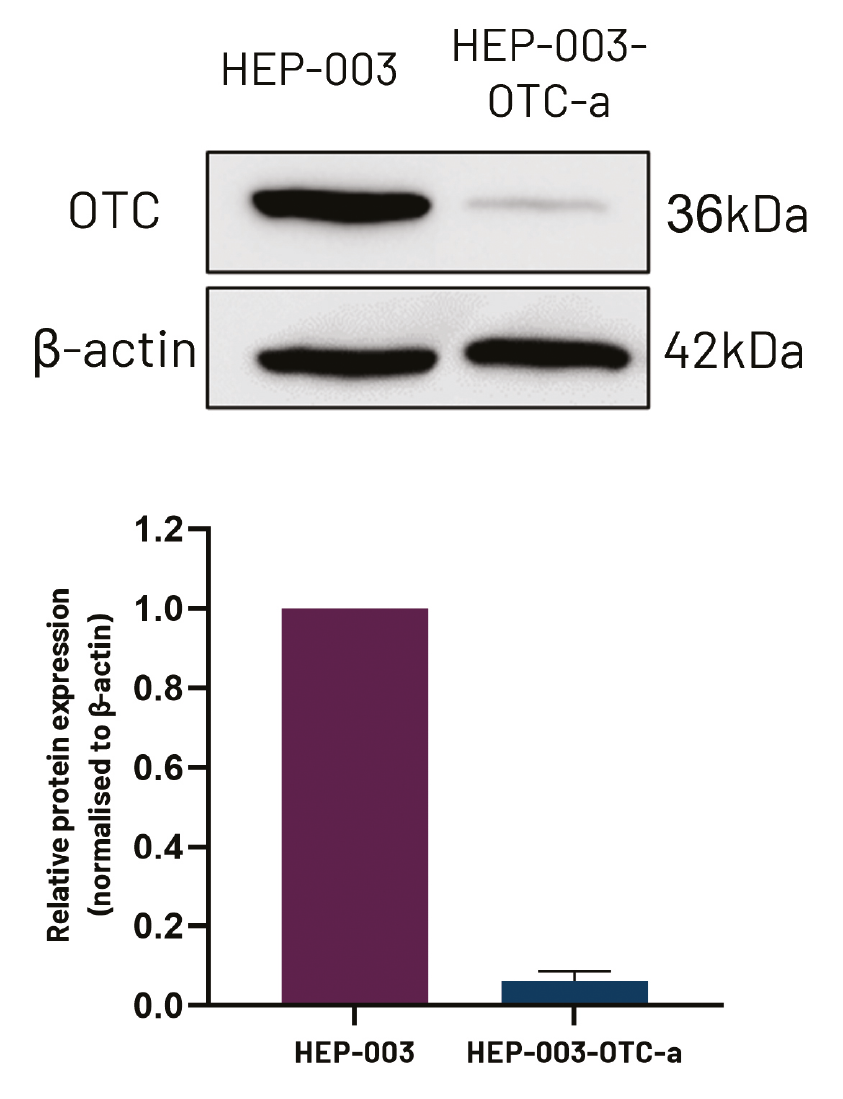
Figure 6. Protein expression levels of OTC in wild-type iPSC-derived iPSCs (HEP-003) and CRISPR-derived OTCD hepatocytes (HEP-003-OTC-a). Data were normalised to beta actin and are presented as mean±SEM of n=3 biological replicates.
DefiniGEN CRISPR-derived OTCD iPSC-derived hepatocytes demonstrate decreased OTC protein expression and urea secretion compared to wild-type iPSC-derived hepatocytes
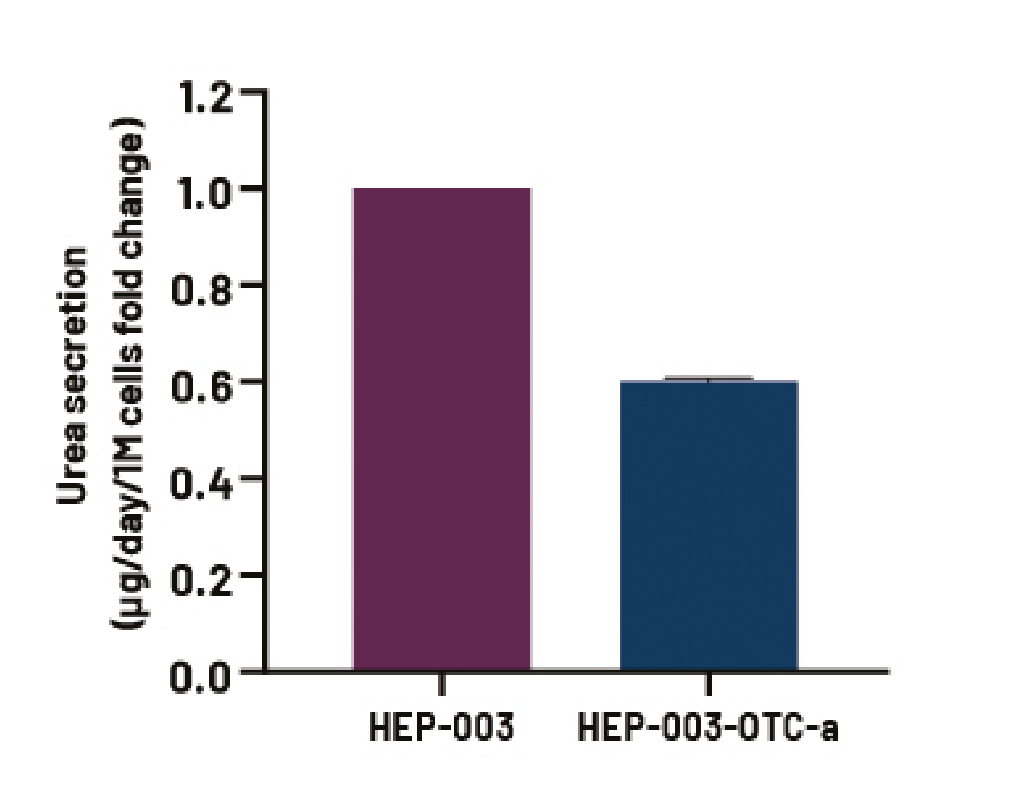
Figure 7. Media urea levels in wild-type Ulti-HEP (HEP-003) and CRISPR-derived OTCD Ulti-HEP (HEP-003-OTC-a). Data were normalised to total cell number and are presented as mean±SEM fold change of n=2 biological replicates.
Conclusion
This case study demonstrates, for the first time, a fully functional urea cycle pathway in wild-type iPSC-derived hepatocytes (Ulti-HEP) and reveals the superiority of DefiniGEN iPSC-derived hepatocytes compared to liver carcinoma HepG2 cells. Supporting these findings, we demonstrate functional OTC activity, with a >30% increase in urea secretion when cells are stimulated with 1 mM NH4Cl and 1 mM ornithine (OTC substrate). Informed by these data, and by applying CRISPR gene editing on DefiniGEN wild-type iPSCs, we have successfully generated an OTC deficiency (OTCD) iPSC line carrying the pathogenic, missense mutation D175V. This CRISPR-engineering OTCD iPSC line can differentiate equally well towards Ulti-HEP, without any compromise in the expression of hepatocyte maturity markers (ALB, A1AT). Crucially, and upon differentiation, the OTCD Ulti-HEP reveal decreased protein expression of OTC and decreased urea formation compared to their isogenic controls, demonstrating their ability to serve as a platform for primary screening activities.
Related case studies:


