iPSC-derived cell products
We provide Wild-Type and disease model Hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate cells, along with Intestinal Organoids, to support your research needs
At DefiniGEN, we specialize in creating iPSC-derived Wild-Type and disease liver models that are highly characterized and mature to support pre-clinical research into liver and metabolic disease models.
Our cells overcome the limitations of traditional liver models such as primary cells, animal models and immortalized cell lines by:
- Removing any batch-to-batch variation as our cells are sourced from a single donor.
- Scaling to meet your needs, unlike primary cells we can create as many cells as you need from a single donor.
- Giving researchers cell models with longer lifespans, our cells can last for approximately 20 days unlike primary cells that typically last less than a week in culture.

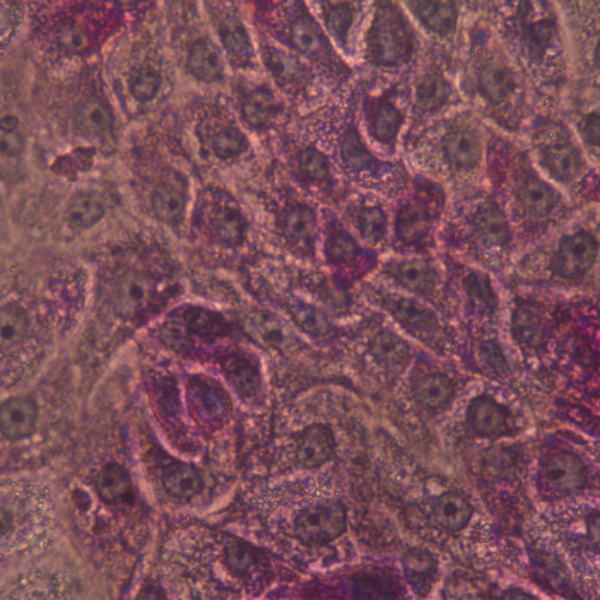
iPSC-derived Human Hepatocytes: Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1 Alpha
DefiniGEN provides iPSC-derived Glycogen Storage Disease Type 1 Alpha (GSD1A) hepatocytes that are suitable to study disorders related to glycogen storage. This genetic disease results from a deficiency in the glucose-6 phosphatase (G6P) enzyme which impairs the ability of the liver to produce free glucose from glycogen.
These cells can offer disease modeling and drug discovery researchers a tool to develop new therapies for this and similar lysosomal storage diseases or to further the understanding of the disease mechanisms.
We offer two patient lines with different genotypes: homozygous R83C in G6PC and compound heterozygous with G222R and Q347X mutations in G6PC.
Cryopreserved & hydrogel-based encapsulated cells
We offer our cell products in two formats, both as cryopreserved vials which can be shipped directly to your lab and in a hydrogel-encapsulated, live plate format.

Cryopreserved cells
If you would like to learn more about how many cells per vial we offer for our cell products, or request a sample certificate of analysis, please contact one of our experts here.

Hydrogel-based encapsulated cells
Hydrogel-based encapsulation of Ulti-HEP and disease models
- We can also transport Ulti-HEP and disease models by encapsulating them in Aterlerix’s hydrogel in 96-well plates under normoxic conditions
- This allows for the transport of plates over long distance for large-scale screening, efficacy and predictive toxicology studies
- This live plate format removes the variation introduced by the cryopreservation and thawing process
- Hydrogel-based encapsulation of cells shows comparable cell viability to non-encapsulated cells and comparable expression of hepatocyte maturity markers (ALB, A1AT and HNF4A)
Explore our Wild-Type cell products
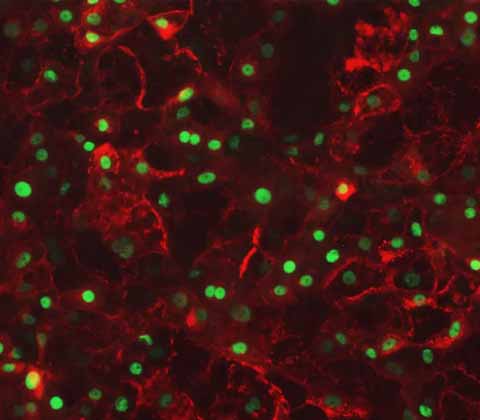
Ulti-HEP:
iPSC-derived Human Hepatocytes
DefiniGEN's iPSC-derived Wild-Type hepatocytes remain functionally stable over a prolonged period of time in culture, making them ideal for drug discovery, drug metabolism and in toxicology screening investigations.
Additionally they express key hepatocyte markers at similar levels to primary human hepatocytes, making them an effective model for in vitro studies.
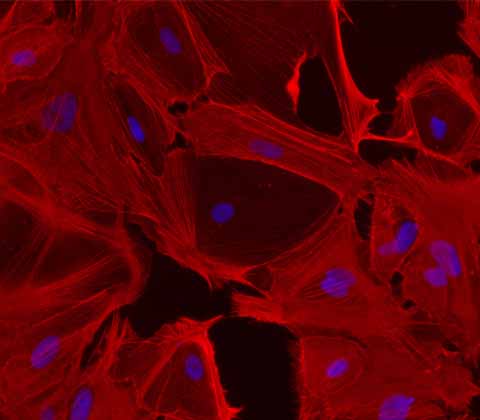
Ulti-HSC:
iPSC-derived Human Hepatic Stellates
Introducing the first commercially available iPSC-derived human hepatic stellates, our Ulti-HSC are ready for large-scale screening of antifibrotic drugs and in vitro disease modelling.
Unlike primary cells, our hepatic stellate cells are derived from a single donor, ensuring no donor-to-donor variation and providing researchers with reproducible results. Our cells are scalable, unlike primary cells, so that we can meet your needs and facilitate more efficient and effective drug discovery whilst reducing the need for animal models.
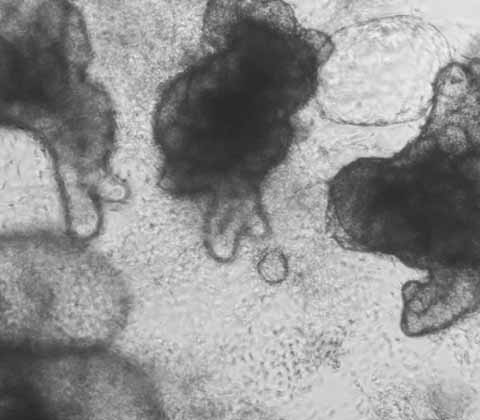
Wild-Type:
iPSC-derived Human Intestinal Organoids
DefiniGEN's iPSC-derived Wild-Type Intestinal Organoids provide a unique in vitro system to model the human intestine.
The organoids display a polarized epithelium and harbor a mixture of cell types normally present in the primary intestinal epithelial barrier in vivo, including goblet cells, Paneth cells, enterocytes and enteroendocrine cells. The cells can be used for drug absorption, metabolism and the modeling of infectious disease.
Explore our Disease Models
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) model
When our Ulti-HEP (Wild-Type hepatocytes) are treated with high glucose or high fat diets, they demonstrate increased lipid accumulation, insulin resistance, lipotoxicity and inflammation. This makes them an accurate and ideal human-derived model to screen compounds in high-throughput investigations.
We also offer iPSC-derived MASLD hepatocytes that have been edited to include some of the most common genetic variants implicated in the disease. One of the lines includes the missense homozygous mutation I148M in the gene coding for Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) and another line harbors the homozgyous E167K mutation in the gene encoding for Transmembrane 6 Superfamily Member 2 (TM6SF2).
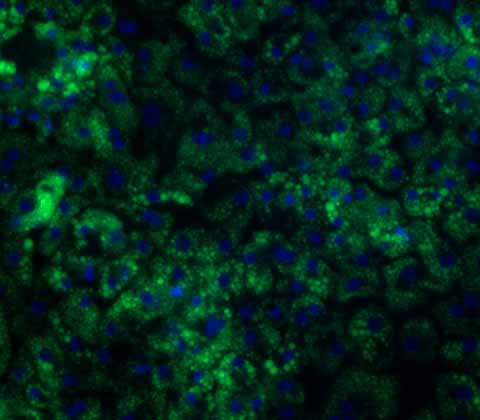
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency model
Our iPSC-derived Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (A1ATD) hepatocytes are highly functional and showcase a strong diseased phenotype in vitro.
Cells are derived from either A1ATD patients or generated through CRISPR engineering and carry the 'Z' (E342K) point mutation in the SERPINA1 gene. This mutation leads to the accumulation of polymeric aggregates of the proteins that ultimately cause liver and lung damage. Our A1ATD hepatocytes represent an optimized disease model for drug discovery applications and are an effective tool for elucidating the underlying mechanisms of the disease.
We also offer homozygous patient-derived A1ATD cells and both homozygous and heterozygous CRISPR-engineered A1ATD lines.
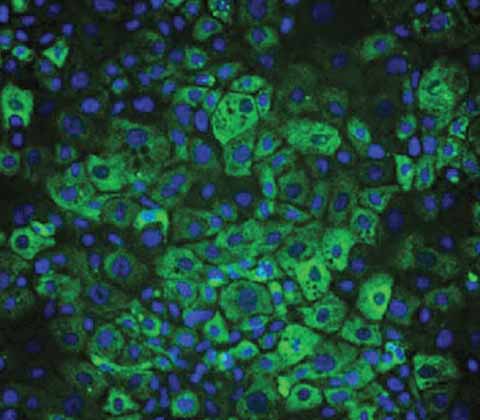
Wilson's Disease model
DefiniGEN's iPSC-derived Wilson's Disease (WD) hepatocytes provide a highly characterized disease modeling platform to study this rare disease.
Cells are generated through CRISPR engineering and carry the homozygous H1069Q mutation in the ATP7B gene. This mutation causes a decrease in the protein function and leads to excessive accumulation of copper that can cause damage to the liver, brain and other vital organs. Our iPSC-derived WD hepatocytes are a powerful tool for drug discovery applications and can help investigate this monogenic disease and other conditions related to oxidative stress.
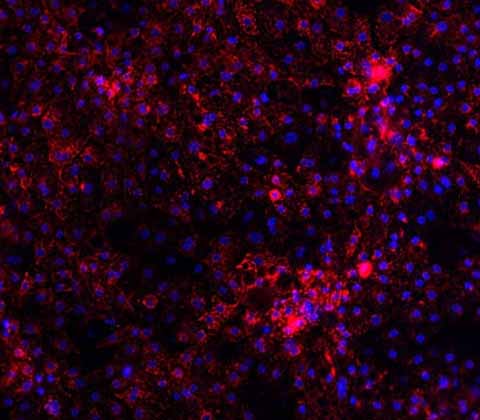
Urea Cycle Disorder models
Using our Wild-Type Ulti-HEP and CRISPR technology, we have created two different disease models: Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) and Citrullinemia.
Our OTCD disease model carries the D175V mutation (GAT>GTT) on the OTC gene and decreased OTC protein expression and urea secretion compared to Wild-Type Ulti-HEP. The Citrullinemia disease model carries the G390R mutation (GGG>AGG) in the ASS1 gene. This model demonstrates decreased ASS1 protein expression compared to Wild-Type Ulti-HEP.

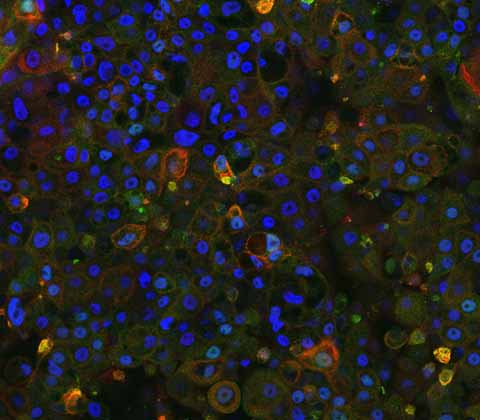
Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis Type 2 (PFIC2) disease model
Our novel, iPSC-derived PFIC2 model, is created using CRISPR-Cas9 technology and is the first of its kind to accurately replicate the PFIC2 phenotype in vitro.
This iPSC-derived model exhibits relevant biological characteristics, ensuring reproducible data without any batch-to-batch variation, making them an ideal tool for drug screening and gene delivery system testing. DefiniGEN’s PFIC2 model allows for large-scale and phenotypically accurate screening of potential treatments, providing a critical resource for advancing therapeutic development for this devastating liver disease.

Get in touch today
Learn more about our cell products, or talk to one of our experts today

